Dynatrace via kubectl
In this step we’ll use the command line to install the Dynatrace Operator.
Deploy Dynatrace
Create a namespace for Dynatrace.
kubectl create namespace dynatrace
Get the configuration for Dynatrace.
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/Dynatrace/dynatrace-operator/releases/latest/download/kubernetes.yaml
The apply command in kubernetes creates and manages resources following a yaml file. It’s a common way to add & configure a number of components at once.
a yaml (Yaml Ain’t Markup Language) file is a text file format designed to be easy to write and read later. It’s powerful and simple- but does require the writer to pay attention to tabs and spacing. The writer should also be prepared to cry at times when they need to get something done quickly and the format is being extra persnickety.
(Optional) Watch the deployment as it progresses.
kubectl -n dynatrace logs -f deployment/dynatrace-operator
the logs command lets us watch the deployment as it rolls out.
Connect to Dynatrace
Once the deployment is finished- use the API_TOKEN and PAAS_TOKEN you created in the Prerequisites to replace the values below.
kubectl -n dynatrace create secret generic dynakube --from-literal="apiToken=API_TOKEN" --from-literal="paasToken=PAAS_TOKEN"
This command creates a new secret named dynakube (used shortly) that allows kubernetes to establish a connection to your Dyantrace tenant.
Next we need to configure options. Download a template to follow:
curl -Lo cr.yaml https://github.com/Dynatrace/dynatrace-operator/releases/latest/download/cr.yaml
Edit the template:
nano cr.yaml
Nano is a text editor built into Ubuntu.
Using arrow keys, navigate to the apiUrL line and update it as shown (replace x’s with your ID)
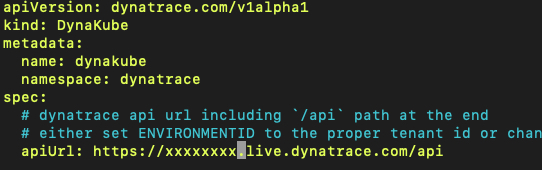
That’s all we need to update for now. If you’re interested, you can check out all parameters.
Save with ctrl+x, Y for yes, and enter to overwrite the template.
Awesome! Almost there. Now we need to apply our customization:
kubectl apply -f cr.yaml
You should see a response simliar to dynakube.dyntrace.com/dynakube created.
Next Steps
Now that you have Dynatrace connected to kubernetes, check out the demo applications and showcases you can deploy in step 5.
Throwing out this ingredient
If you want to recycle this ingredient for any reason, simply follow the two steps below.
Remove the component you installed.
kubectl delete -n dynatrace dynakube --all
and run the delete command to reverse the apply command.
kubectl delete -f https://github.com/Dynatrace/dynatrace-operator/releases/latest/download/kubernetes.yaml